How Is an STD Test Conducted?
Last updated: Dec 22, 2025
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are
diagnosed through blood tests, urine samples, or
swabs taken from the genital or throat area. In Singapore, these tests are offered at
public healthcare facilities, private clinics, and MOH-regulated STD clinics.
Because many STIs can present without
symptoms, early testing allows you to protect your health and prevent spread to
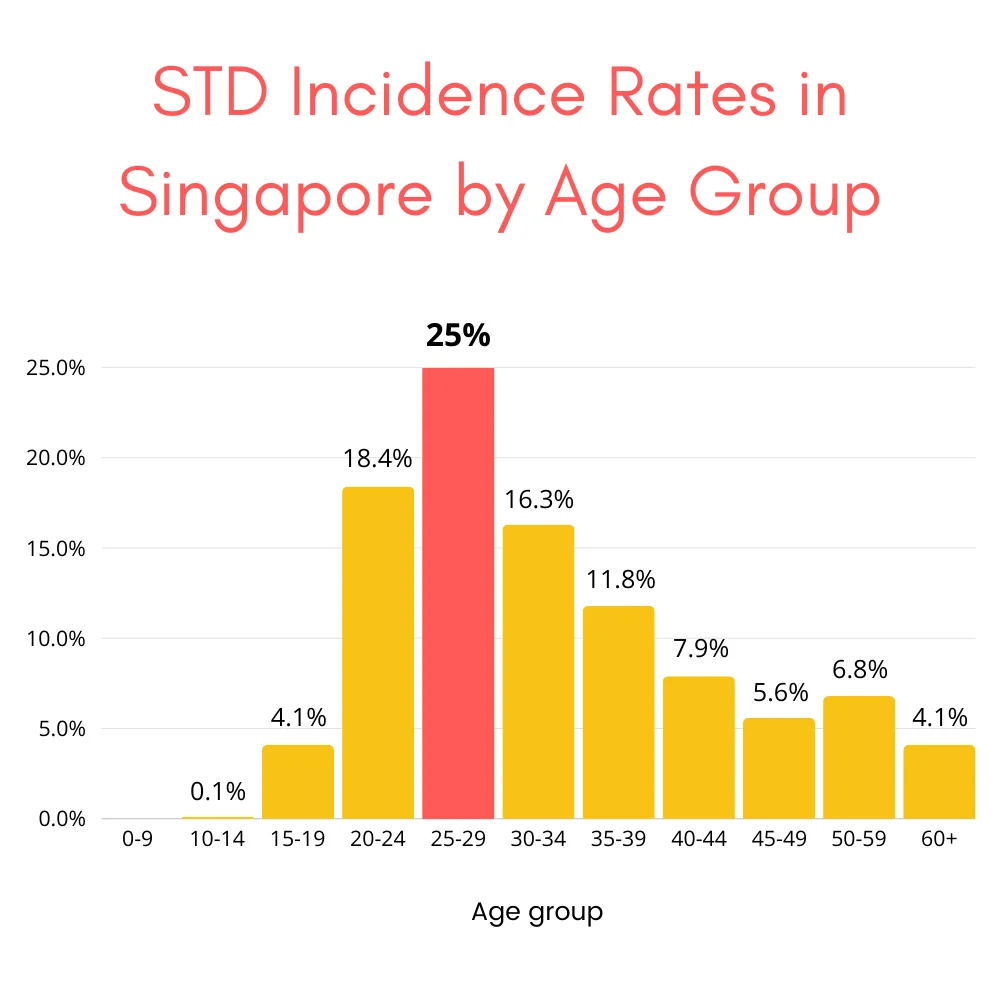
your partners. This is especially important for young adults, who have the highest rates of
sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in Singapore, according to a 2017 Ministry of Health
report.

Common STD Testing Methods
Most STDs, active (with symptoms) or dormant (asymptomatic), can be detected through blood, urine or swab testing:
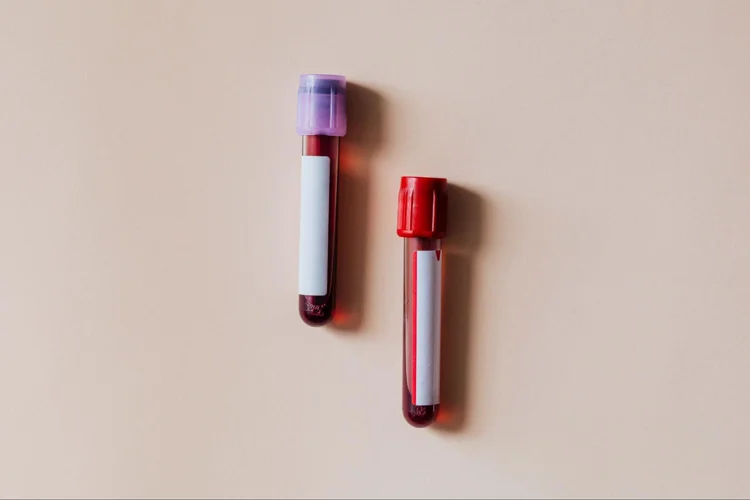
Blood Tests
Blood tests detect the presence of antibodies (proteins your body produces to fight
infection) or foreign substances (antigens) produced in response to an STD infection. These
tests can identify bacterial or viral DNA/RNA, surface antigens of the virus or bacteria,
and antibodies. However, it's important to note that blood tests typically detect past or
current infections, not necessarily active disease.
STDs tested for through blood tests may include human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV), syphilis,
herpes, hepatitis.
Urine Tests
Urine tests detect the DNA of bacteria causing the infection. The urine sample is analysed
using tests that amplify the genetic material of the bacteria (Nucleic Acid Amplification
Tests or NAATs).
Common STDs tested for through urine tests include chlamydia
and gonorrhoea.
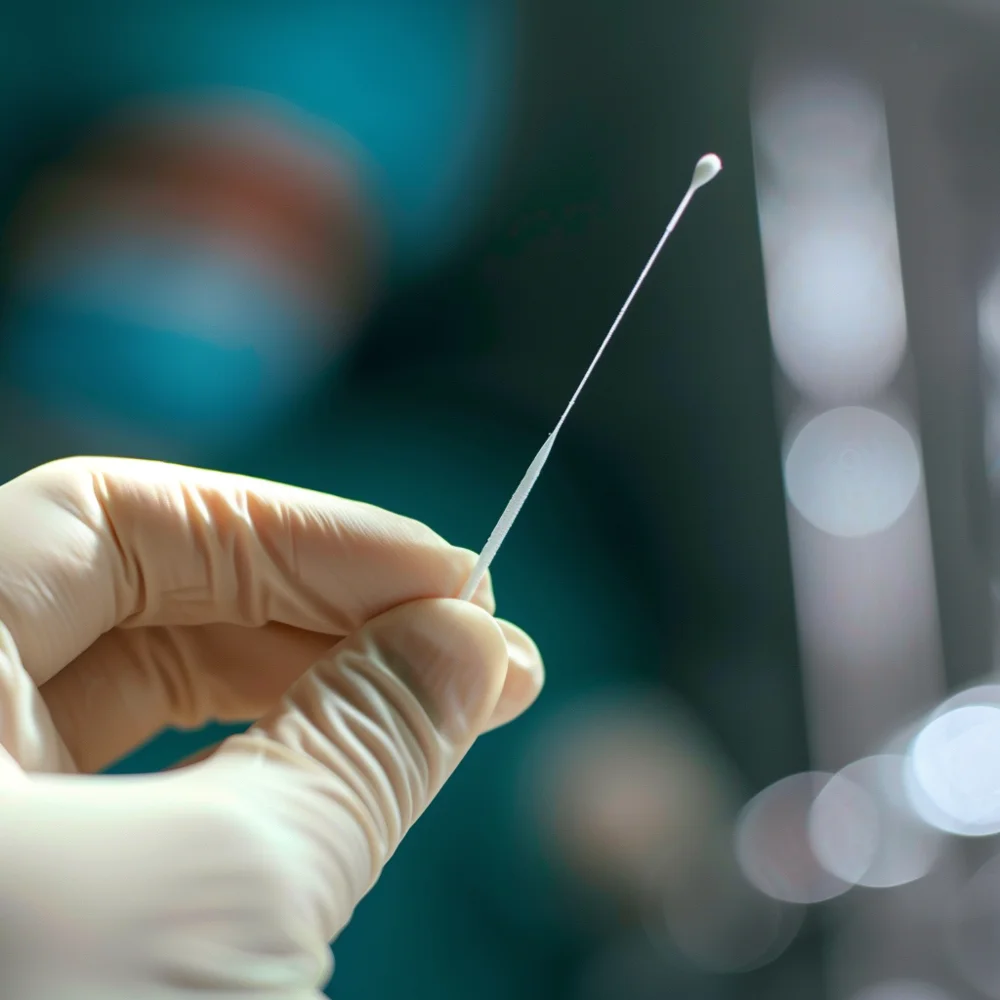
Swab Tests
Swab tests collect samples from specific body parts (cervix, urethra, rectum, throat, or
sores) to detect the presence of bacteria or viruses. Samples are analysed using various
testing methods, such as NAATs and viral cultures (growing the virus in a lab).
Common STDs tested for through swab tests include chlamydia and gonorrhoea, herpes, human papillomavirus
(HPV).
Oral Fluid Tests
Oral fluid tests involve collecting saliva samples, which are then analysed for antigens
(parts of the virus) or antibodies (proteins produced by the body to fight
infection).
One of the common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) tested for using oral fluid tests is
HIV.
Multiplex PCR
Multiplex PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a testing method that can simultaneously detect
multiple STDs from a single sample (blood, urine and/or swab) with high accuracy. This
method is beneficial for comprehensive screening, especially for individuals at higher risk
of multiple infections. Multiplex PCR can save time and resources compared to individual
tests for each STD.
It is best for you to consult with your doctor to determine the best testing approach for
you.
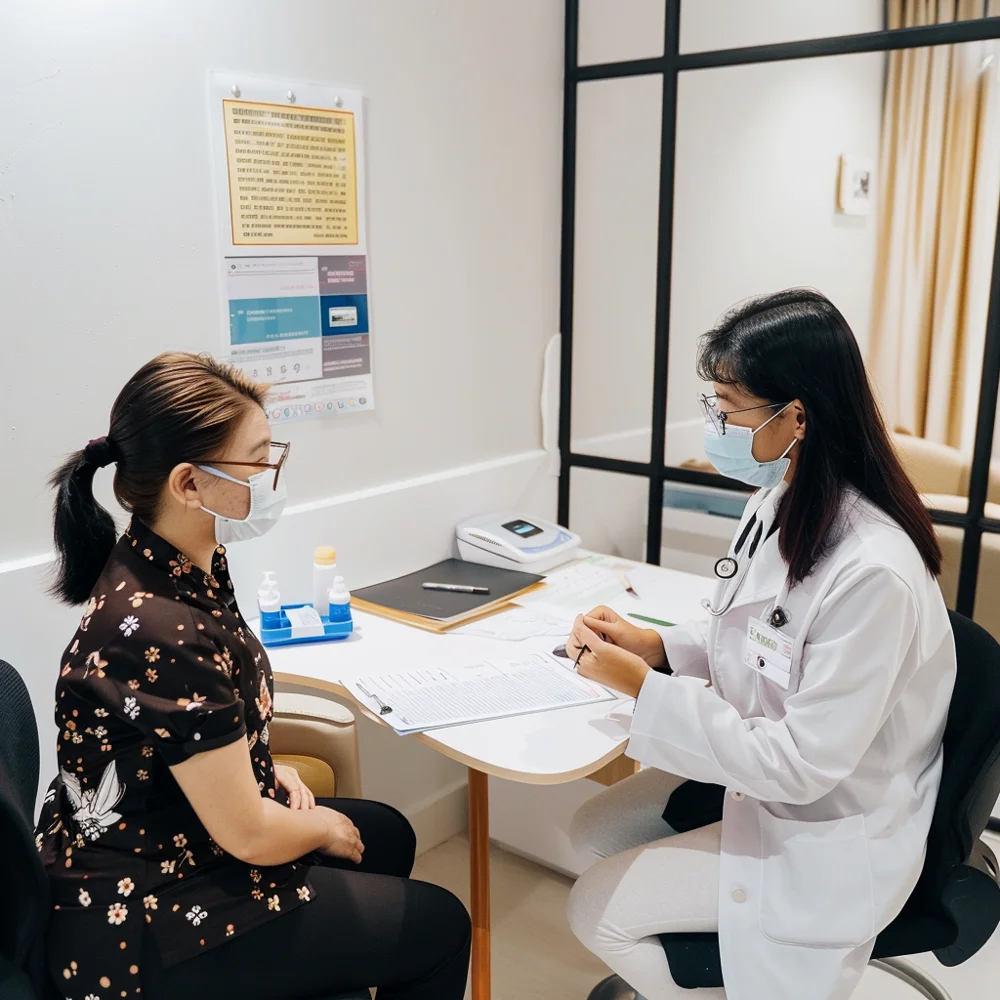
The Testing Procedure
The procedure for an STD Test at a clinic typically involves:
- Consultation: The doctor will discuss your symptoms, sexual history, and any specific concerns you might have. The consultation is kept strictly confidential and private.
- Sample Collection: Depending on the type of test, samples may be collected through blood, urine, or swabs from the genital area, throat, or rectum.
- Laboratory Analysis: Collected samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Results: Results are typically available within a few days, depending on the specific tests conducted.
What to Expect During Your Visit
When you go for STD testing, clinics provide a professional, non-judgmental, and
confidential environment. Doctors and staff are trained to handle sensitive issues with care
and discretion. Strict protocols including secure electronic health records and discreet
communication methods are employed, ensuring your personal information and test results are
not shared without your explicit consent. These strict protocols guarantee that your
information remains confidential throughout the testing process and beyond.
Disclaimer: This article is not representative of the testing process at
all clinics, and your experience might differ.

Post-Test Counselling
Post-test counselling is an integral part of the STD testing process. Your doctor will explain the results, answer questions, provide emotional support if required, and outline next steps for treatment or further testing. While STD tests are highly accurate, there is still a chance of a false positive (i.e., a test indicating an infection is present when it is not). If this is a concern, your doctor may recommend confirmatory testing with more precise methods.
- Positive Results: Follow-up appointments are crucial for discussing treatment options, such as antibiotics for bacterial infections and antivirals for viral infections, as well as preventive measures. Continuous monitoring and follow-up tests may be necessary to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Negative Results: Your doctor may offer prevention advice and suggest a schedule for future testing to ensure continued sexual health.

Summary
Regular STD testing is essential for maintaining sexual health and preventing the spread of infections within the community. By understanding the testing process, you can make informed decisions about your health. Regular testing and practising safe sex are key steps in contributing to a healthier Singapore. Take charge of your sexual health and schedule an appointment with a doctor to test for STDs today.
Why Choose ATA Medical?







Delivering Care Patients Appreciate
What to Expect
FAST RESULTS
We strive to deliver your results within 7 working days.
MINIMUM WAITING TIME
Our patient-oriented processes ensure your waiting time is kept to a minimum.
Friendly Service
Service is a top priority for us at ATA Medical.
Email Us at camden@atamed.sg for more
information.
Book your STD screening with us at 88750352


