How Do STDs Spread?
Last updated: Dec 20, 2025
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) spread through
several routes, with sexual contact and intimate physical activity being the most common.
Knowing how these infections pass from person to person is key to protecting yourself and your
partners through informed choices. This is especially important as some STDs are highly
contagious and have no cure.
If you are
sexually active, routine STD
screening is recommended to safeguard your health.
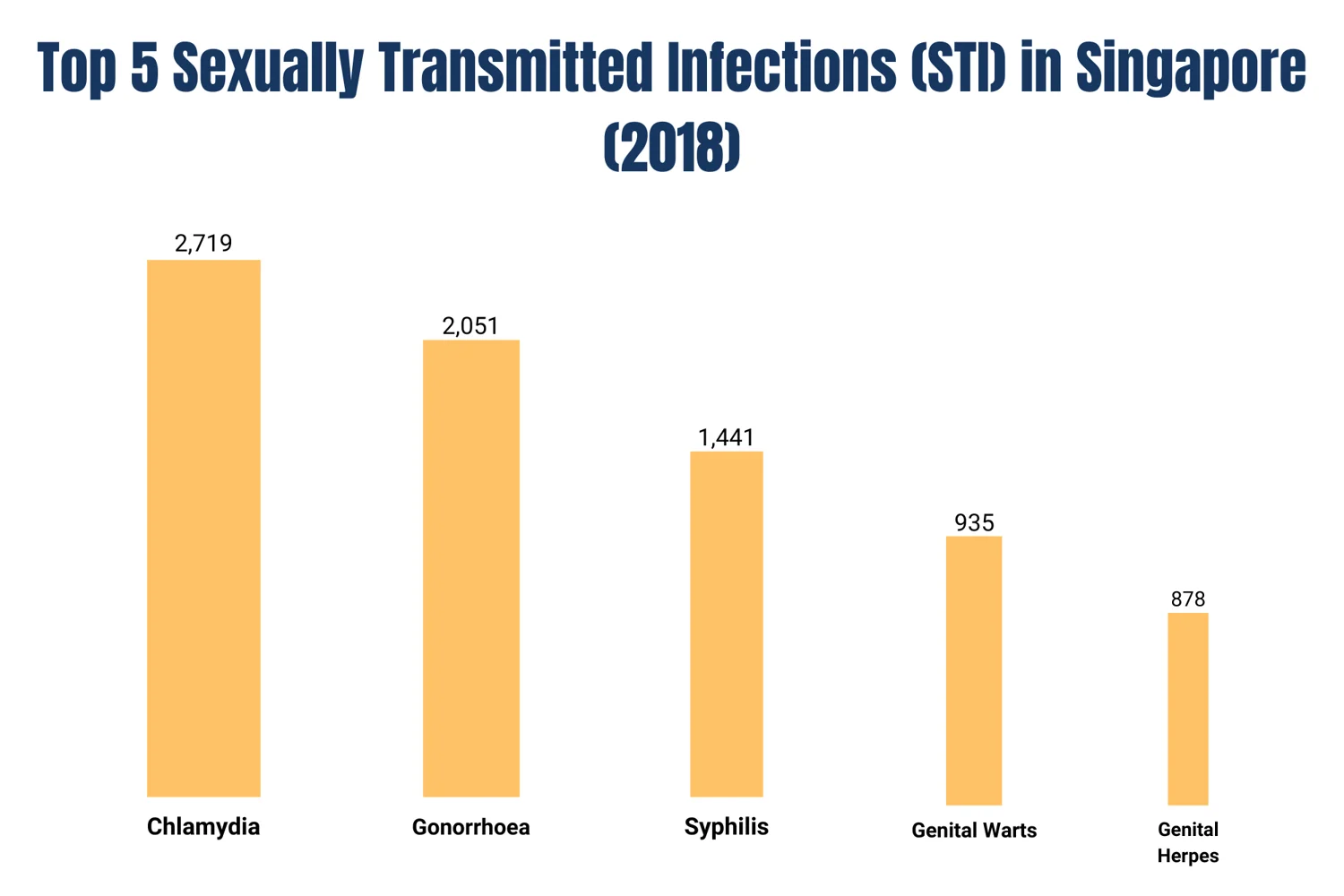
Common Modes of STD Transmission
Sexual Contact
The primary mode of STD transmission is through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. During these activities, the exchange of body fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions, and blood can transmit infections like chlamydia, gonorrhoea, trichomoniasis, and hepatitis B. Additionally, skin-to-skin contact with infected areas, such as sores or lesions, can spread infections like syphilis, herpes, and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Blood Transfusion and Needle Sharing
Infections like HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C can be transmitted through contact with contaminated blood. This usually happens when sharing needles or syringes for drug use, or when equipment used for tattoos or piercings is not properly sterilised.

Mother-to-Child Transmission
Pregnant women with STDs can pass infections to their babies during childbirth or breastfeeding, a process known as vertical transmission. This can lead to serious health issues for the newborn, highlighting the importance of prenatal screening and treatment.
Other Bodily Fluids
STDs such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis, and herpes can spread through saliva in an infected person's mouth or throat although the risk of transmission is lower compared to sexual contact.

Myths About STD Transmission
Myth: You can get STDs from toilet seats, or hugs and handshakes.
Fact: STDs are not spread through casual contact. These infections require
direct contact with infected bodily fluids like semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
However, some STDs such as herpes are present in saliva and can be transmitted between
individuals through deep and wet kissing. Organisms causing STDs are typically not
able to survive
outside the body.
Myth: Only those who are sexually active with multiple partners get
STDs.
Fact: Anyone who is sexually active can get an STD, regardless of the
number of partners. Using protection and getting regular screenings are key preventive
measures.

Myth: You can tell if someone has an STD by looking at them.
Fact: Many STDs do not show visible symptoms. The only way to know for sure is
through testing.
Myth: Once you've had an STD, you're immune to it.
Fact: Having an STD once does not protect you from getting it again. Reinfection is
possible, so it is important to take precautions.
Myth: Birth control pills protect against STDs.
Fact: Birth control pills only work to prevent pregnancy. They do not offer any
protection against STDs. Using condoms is necessary to reduce the risk of STD transmission.
Preventive Measures and Practices
Effective prevention strategies can include:
- Using Protection: Consistent and correct use of protection such as condoms and dental dams during sexual activity significantly reduces the risk of STD transmission.
- Vaccination: Vaccines are available for certain STDs, such as HPV and hepatitis B, providing long-term protection.
- Regular Testing: Regular screening for STDs helps in early detection and treatment, reducing the risk of complications and further transmission. For those who prefer privacy, teleconsultation services are available.
- Safe Practices: Avoiding sharing needles and syringes. Ensure any medical or cosmetic procedures are done with disposable or sterilised equipment. Find out about the sterilisation process before undergoing any such procedures.

Summary
Understanding how STDs spread empowers individuals to make informed choices and take control of their sexual health. By adopting safe practices like consistent condom use, getting vaccinated for preventable STDs, and undergoing regular testing, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting and transmitting infections. If you suspect you may have been exposed, it is strongly recommended to get tested for STDs.
Why Choose ATA Medical?







Delivering Care Patients Appreciate
What to Expect
FAST RESULTS
We strive to deliver your results within 7 working days.
MINIMUM WAITING TIME
Our patient-oriented processes ensure your waiting time is kept to a minimum.
Friendly Service
Service is a top priority for us at ATA Medical.
Email Us at camden@atamed.sg for more
information.
Book your STD screening with us at 88838892


